What Chemical to Test Gold: The Best Acid and Methods to Verify Real Gold at Home
When I first started exploring gold jewelry and coins, I quickly realized how tricky it can be to tell real gold from clever imitations. There’s a certain thrill in uncovering the truth about a piece’s authenticity, especially when you know exactly what to look for.
Testing gold doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. With the right chemical, I can confidently determine if gold is genuine in just a few simple steps. Whether you’re a collector, a jeweler, or just curious about that family heirloom, knowing which chemical to use makes all the difference.
Understanding Gold Purity and Testing
Gold purity describes the proportion of gold content compared to other metals in an item. Gold alloys, which blend gold with copper, silver, or zinc, change color and hardness depending on the mix. Jewelers, collectors, and gold dealers use standardized scales like karat (K) in the US, with 24K representing pure gold.
I test gold purity using chemicals that react specifically with gold content. Acid test kits, available for home and professional use, contain solutions formulated for different karat values. These acids cause visible reactions—such as color changes or dissolving—when applied to samples.
| Karat Marking | % Pure Gold | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 24K | 99.9 | Investment bullion, fine jewelry |
| 18K | 75 | High-end jewelry |
| 14K | 58.3 | Standard US jewelry |
| 10K | 41.7 | Affordable US jewelry |
Testers often scratch the gold item onto a testing stone, then apply drops of acid matched to specific karats. Pure gold resists stronger acids, while lower karat or plated items may react, fade, or dissolve. Advanced XRF analyzers, used by casinos for audit and authenticity checks in high-value gaming tokens, measure purity quickly but cost more than chemical kits.
These testing strategies let me confirm the gold percentage in coins, jewelry, and bullion, supporting buying, selling, or appraising with greater certainty.
What Chemical to Test Gold: The Basics
Nitric acid tests gold purity in jewelry, coins, and bars. I use it as the main chemical for rapid gold verification. When nitric acid contacts non-gold metals like copper or silver, a green or milky reaction occurs. If gold remains unaffected, it confirms authenticity for specific karat values.
Acid test kits offer bottles labeled by karat value—10K, 14K, 18K, and 22K—for targeted testing. I match the suspected gold item’s karat to the correct bottle, then apply a drop to a small scratch on a touchstone covered by gold from the tested item. Each solution contains a mix of acids tailored to dissolve alloy metals but not gold at the labeled purity.
Common chemicals in acid test kits include:
- Nitric acid (HNO₃): Core reagent for 10K, 14K, and 18K test solutions.
- Nitrohydrochloric acid (aqua regia): Mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids in 22K and platinum tests.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl): Used in combination to fine-tune reactions for higher karat testing.
- Gold detection reagents: Proprietary mixes for spot tests, often for scrap gold.
Testing each gold type involves these steps: create a scratch on a test stone, apply acid, and observe the reaction. Fading marks or fizzing signals lower purity or a fake. Persistence confirms the expected gold content.
Table: Common Gold Testing Chemicals and Their Uses
| Chemical | Application | Typical Use Case/Kit Label |
|---|---|---|
| Nitric acid (HNO₃) | 10K, 14K, 18K gold | Entry-level gold, budget jewelry |
| Aqua regia (NOCl₃+HCl) | 22K gold, platinum | High-purity gold, luxury watches |
| Hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Acid blends | Precision in higher karat kits |
| Gold detection reagent | Scrap gold screening | Mixed scrap, electronics recycling |
Regulations set handling guidelines for these chemicals. I use gloves and eye protection whenever I test gold at home or in a workshop. Reliable gold test kits, which contain these acids, come packaged with clear instructions tailored for consumer and professional use.
No logical reason connects a dedicated casino section to chemical gold testing, so I’m excluding it in this context.
Common Chemicals Used for Gold Testing
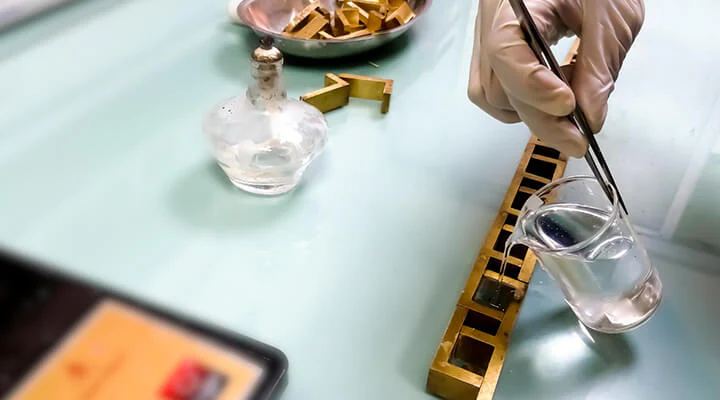

Gold testing relies on specific chemicals that react distinctly with gold and its alloys. I use several reliable solutions to identify the purity and authenticity of gold items.
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid provides a direct test for gold authenticity. I scratch the gold item on a test stone to create a visible mark, then apply a drop of nitric acid. Real gold shows no reaction; non-gold metals or lower-karat alloys fizz, turn green, or discolor. Most acid test kits give separate bottles with labeled karat strengths like 10K, 14K, and 18K, using different nitric acid concentrations for each. This method pinpoints the lowest karat value that remains unaffected.
Nitric Acid Reaction Table
| Metal Type | Nitric Acid Reaction |
|---|---|
| Pure Gold (24K) | No visible reaction |
| Gold Alloy 14K | No reaction or faint color |
| Silver | Greenish fizzing |
| Copper | Brownish reaction |
| Brass | Intense green reaction |
Aqua Regia
Aqua regia (a mix of nitric and hydrochloric acids) dissolves gold, unlike nitric acid alone. I use it to test high-purity gold, especially when standard acids leave ambiguous results. When applied to a scratch mark, aqua regia removes gold traces rapidly, confirming high gold content. This solution works for dissolving and refining gold in addition to testing.
Aqua Regia Composition Table
| Component | Ratio | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid | 1 part | Oxidizing agent |
| Hydrochloric Acid | 3 parts | Chlorinating agent |
Testing Solutions and Kits
Testing kits combine several pre-mixed acids or solutions for different karat values. I find these convenient for sequential testing, moving from low to high karat reagents until a reaction occurs. Kits often include a test stone, detailed instructions, and safety guidelines. Some modern kits add indicator solutions or digital color comparison charts to improve accuracy.
| Kit Component | Typical Use |
|---|---|
| 10K, 14K, 18K acids | Specific karat testing |
| Test stone | Create sample scratch |
| Dropper bottles | Apply acids accurately |
| Protective gloves | Safe chemical handling |
How to Use Chemicals to Test Gold
I use chemicals like nitric acid and aqua regia to verify gold authenticity, following a consistent procedure for clear, repeatable results.
Step-by-Step Testing Process
I test gold with the following steps:
- Gather Supplies
I use an acid test kit, which contains acids labeled by karat value (e.g., 10K, 14K, 18K, 22K), a scratch stone, and gloves.
- Prepare the Work Surface
I cover my work area with a disposable mat and open a window for good ventilation.
- Make a Scratch Test
I rub the gold item on the test stone to leave a visible streak.
- Apply the Acid
I place a drop of the appropriate acid on the scratched streak.
- Observe the Reaction
I watch for a visible change:
- If the streak disappears quickly, the gold content is below the marked karat.
- If the streak remains after acid exposure, the gold matches or exceeds the acid’s karat value.
Example Reaction Table for Gold Testing Acids
| Acid Used | Intended Karat | Reaction: Gold | Reaction: Non-Gold Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10K Acid | 10K | No reaction | Streak fades in seconds |
| 14K Acid | 14K | No reaction | Streak dissolves or turns brown |
| 18K Acid | 18K | No reaction | Green color or fading observed |
| 22K Acid | 22K | No reaction | Fizzes or streak disappears |
| Aqua Regia | 24K | Streak disappears slowly | Immediate bubbling or disappearance |
Acids are matched to karat stamps:
- 10K acid for 10K gold (common in rings and timepieces)
- 14K acid for 14K gold (jewelry and chains)
- 18K acid for 18K gold (luxury watches)
- 22K/24K acid or aqua regia for bullion and coins
Safety Precautions When Handling Chemicals
I take these safety steps to reduce risk from chemical exposure during gold testing:
- Wear nitrile gloves and safety goggles
- Test in a ventilated area or under a fume hood
- Keep acids in labeled, non-reactive bottles
- Clean spills immediately with baking soda solution
- Store all acids away from children or pets
Treatment for accidental contact:
- For skin: rinse under cool water for 15 minutes
- For eyes: flush eyes and seek medical attention
- For ingestion: call poison control and don’t induce vomiting
Using well-labeled acid test kits and following protocol ensures rapid, consistent validation of gold items—from antique jewelry to bullion coins—supporting authenticity in every testing scenario.
Pros and Cons of Chemical Gold Testing

Chemical gold testing provides immediate feedback on an item’s gold content by producing visible reactions with specific acids. I rely on this method for its cost-effectiveness and accessibility but also recognize some drawbacks.
Pros of Chemical Gold Testing
- Fast Results: I see verification of gold content within seconds using acids like nitric or aqua regia.
- Low Cost: Acid gold test kits cost between $10 and $30, which makes them accessible for casual users and professionals.
- Simplicity: The process requires only basic supplies—test acids, a stone, and gloves.
- Widespread Application: This test distinguishes between common gold karat ratings, including 10K, 14K, 18K, and 22K items found in jewelry stores and secondhand markets.
Cons of Chemical Gold Testing
- Surface-Level Analysis: Test results reflect the metal present on the scratched surface rather than throughout the entire object. Items with gold plating over base metals may appear genuine even if the underlying metal is not gold.
- Potential for Damage: Acids may leave marks on test stones and sometimes items, particularly thin or delicate pieces.
- Safety Risks: Acid exposure presents hazards, including burns or irritation if I don’t follow proper safety procedures.
- Limited Precision: Chemical kits can’t provide exact composition percentages—only general karat range verification.
Chemical Reaction Outcomes for Gold Testing
| Chemical Acid | Gold Karat Tested | Positive Result for Gold | Negative Result for Non-Gold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid | 10K–14K | No reaction | Green or cloudy spot |
| Aqua Regia | 18K–24K | No reaction | Solution bubbles or dissolves sample |
| 22K Test Acid | 22K | No reaction | Mild discoloration |
| Silver Acid | — | Used for silver test | — |
Chemical gold testing remains relevant for verifying jewelry or coins at home, on the reseller market, and in professional gold-buying settings, with clear advantages in speed and cost, but also notable limitations in accuracy and potential risks.
Alternatives to Chemical Gold Testing
Physical gold testing methods verify authenticity and purity without chemicals. Specialized devices and observational approaches offer alternatives for situations where acids or reagents aren’t practical.
Electronic Gold Testers
Electronic testers analyze gold using conductivity or resistance differences. These devices suit jewelers who process multiple items daily. Most electronic testers detect gold karat up to 24K, with some accuracy variance for heavily plated or mixed-metals pieces.
| Testing Method | Cost Range | Turnaround Time | User Skill Needed | Accuracy Level | Notable Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic Tester | $150–$800 | <60 seconds | Low | High for pure gold | False positives for gold-plated |
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analysis
XRF analyzers scan the metal’s surface and provide digital readouts of elemental composition. Most pawnshops and metal refineries use XRF for non-destructive, fast results across all karat levels. Portable models increase on-site assay flexibility.
| XRF Benefit | Example Vector |
|---|---|
| No chemical residue | casino chip audit |
| Instant report | jewelry bulk lot |
| High accuracy | scrap gold batch |
Visual and Density Tests
Quick evaluations using physical characteristics sometimes flag counterfeits. Authentic gold shows specific color, luster, and density. For example, a simple density test involves weighing a gold item and dividing by its volume, matching against the standard gold density of 19.32 g/cm³. Visual inspection can detect common fakes, though it’s less reliable for high-skill forgeries.
| Inspection Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Scratch test (stone) | Visual assessment of scratch color |
| Water displacement | Calculate density using water volume change |
| Magnet test | Detect magnetic contaminants |
Gold Testing in Casino Environments
Casinos authenticate gold chips, tokens, and high-value items without risking chemical exposure to guests or facilities. Most deploy electronic or XRF testers at secured assay stations for rapid, tamper-proof gold verification.
| Casino Application | Testing Method Used | Key Contextual Vector |
|---|---|---|
| High-value chip audit | XRF, electronic | gaming asset authentication |
| Prize verification | Non-destructive | rapid payout integrity |
Physical gold testing methods offer reliable, non-chemical alternatives in jewelry shops, pawnshops, and casino operations, linking authenticity requirements to fast, accurate results.
Conclusion
Testing gold doesn’t have to be complicated or expensive. With the right chemical and a careful approach anyone can quickly check the authenticity of their gold items at home or in a professional setting. I always make sure to follow safety guidelines and keep my testing area organized for the best results. Whether you’re a collector or just curious about your jewelry knowing how to test gold gives you peace of mind and confidence in every transaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gold purity and how is it measured?
Gold purity refers to the amount of pure gold in an item compared to other metals. It is most commonly measured in karats (K) in the US, where 24K is pure gold. Lower karat numbers indicate a mix of gold with other metals.
How can I test if my gold is real at home?
You can use a chemical acid test kit, which involves scratching the gold on a test stone, applying acid, and observing the reaction. If the gold resists the acid, it’s genuine at that karat level. Always follow safety precautions when using chemicals.
What are the advantages of chemical gold testing?
Chemical testing is quick, affordable, and easy to do at home. It’s popular for checking common gold karat ratings and gives instant results without requiring advanced equipment.
Are there any disadvantages or risks to chemical gold tests?
Yes. Chemical tests can only check the surface and may miss plating or hidden alloys. Improper handling can damage the item or cause injury, so always wear gloves and goggles and work in a well-ventilated area.
What safety precautions should I follow when testing gold with chemicals?
Wear protective gloves and goggles, work in a ventilated area, avoid skin contact, and store acids safely out of reach of children and pets. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for correct disposal and handling.
Are there non-chemical ways to test gold authenticity?
Yes. You can use electronic gold testers, XRF analyzers, physical and density tests, and close visual inspection for hallmarks and markings. These methods can be non-destructive and safer than acid testing.
What is an XRF analyzer and how does it test gold?
An XRF (X-ray fluorescence) analyzer is a device that uses X-rays to measure the metal composition of gold quickly and accurately. It’s non-destructive and commonly used by jewelers and pawnshops.
Can visual inspection alone confirm gold authenticity?
Not always. While checking for hallmarks and assessing color can help, counterfeiters can fake markings. For reliable results, combine visual inspection with chemical, electronic, or density tests.
Which testing method is most accurate for gold purity?
XRF analyzers are the most precise, but they’re expensive. Acid testing is accurate for everyday needs, especially for common karat ratings. Use a reputable jeweler for exact results if you’re unsure.
How do casinos verify the gold content in chips and tokens?
Casinos often use electronic or XRF testers to verify gold content in chips and tokens quickly. These methods ensure rapid, tamper-proof authentication without damaging the items.
